INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ACT

COPYRIGHT
The right which given by law for a certain term of years to an author, composer, etc.
- To print
- To publish
- Sell copies of his original work.
Whose Rights are protected?
- Copyright protects the right of the Author, i.e. creator of intellectual Properties.
- She/he is also called the First Owner of Copyright.
- However, in the case of employment, the employer is the first owner of these rights.
- E.g. In the case of musical work composer is the owner of the work.
Why Copyright?
Favor-
- Rewards for creative efforts,
- Protects the interest of the creator.
Against
- Protects corporate interests only,
- Criminalizing legitimate use
Copyright: National Vs International
- No single “international copyright” for the whole world.
- The copyright Act of each country is compliant with most international conventions.
- In India, the Copyright Act of 1957 is complaint with these international conventions and treaties-
- Berne convention of 1886
- Universal Copyright Convention of 1951.
Indian Copyright Act,1957
- First right in 1914
- Now, Indian Copyright Act,1957; w.e.f. 21st Jan 1958
- Further amendments in 1983,1984,1992,1999
- Adopted many English provisions, and also introduced new ideas and concepts.
- Created copyright Office and Copyright Board
- Introduced criminal and civil remedies against infringement.
Indian Perspective on Copyright
The copyright act of 1957 in the following two forms:
- ECONOMIC RIGHTs
- MORAL RIGHTS
Economic Rights:-
Several things attach to the holder of a copyright:
- To publish copies of the work and to sell those copies.
- To import or export the work
- Works that adapt the original work
- To display the work publicly
- To sell and assign these rights to others
- To display by radio or video
Moral Rights:-
- Right of paternity i.e. to claim authorship of work
- To prevent all others from claiming authorship of his work.
- Right of integrity i.e. to prevent distortion, mutilation, or other alterations of his work, or any other action in relation to said work, which would be prejudicial to his honors or reputation.
TERMS OF COPYRIGHT
The general rule is that copyright is for 60 years.
It is continued.
- From the death of the author.
- Literary
- Dramatic
- Musical
- Artistic work
- From the date of publication.
- Cinematograph films
- Sound recordings
- Photographs
- Works of government & international organization
- Poshthumous Publications
Registration of Copyright
- Registration is not mandatory But voluntary.
- Make an application in a prescribed form to the ROC(Registrar Of Copyright).
- The application should make be in triplicate and accompanied by the prescribed fees.
- If no objection to such registration is received by ROC within 30 days of the date or receipt of the application, he shall, If satisfied with the correctness of particulars given in the application, enter such particular in the particular in the Registration Of Copyright.
Copyright Symbol
- Use of the “©” symbol.
- Anyone who claims copyright can use it.
- Not necessary to have a registration to use the designations.
- Highly used for incorporating a copyright notice
- Example:
Copyright @2009 Microsoft Corporation
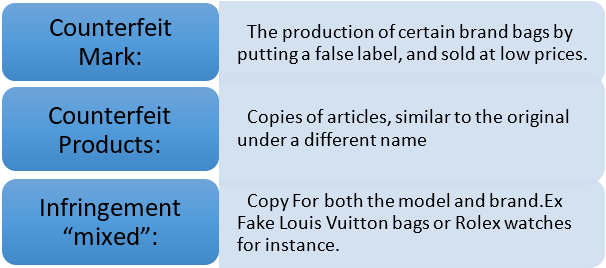
Counterfeiting to Copyright
Remedies of Copyright
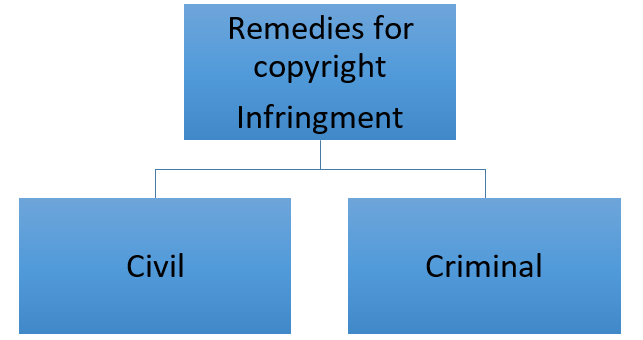
Civil Remedies
- Civil Remedies
- Injunction
- Damages
- Accounts
- Delivery of infringing Copy
- Damages For conversion
Jurisdiction in DISTRICT COURT
Criminal Remedies
- Criminal Offences, if Done knowingly
- Imprisonment
- 6 Months-3 Years
- Fine
- Rs 50,000-Rs2,00,000
Seizure of infringing copies
Conclusion
- Each country has its own law compliant with any international convention.
- Copyright Prevents distribution of Idea.
- It safeguards the interests of the creators.
- It encourages society to do something new.
- Registration is not compulsory.
- Economics rights can be assigned to another person.
- Infringement is a criminal offense if done knowing.
Check this out – What is Marketing?




October 27, 2022
[…] Also check – COPYRIGHT ACT, 1957 – Full Document in English […]